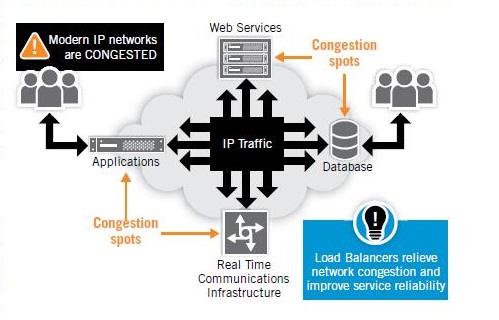
What are some of the use cases for a real-time Application Delivery Controller(ADC)?
In my past blog, I made a case for using the Application Delivery Controller, essentially an intelligent load balancer for web, database, and other network-based traffic, to be applied to real-time telecom communications. Let’s now observe some use cases for a real-time ADC.
1. Application-aware contextual routing
Application aware contextual routing is an important element of a load balancer. It intelligently distributes traffic associated with a service (e.g., SIP) across one or more available service nodes in the network. When key services such as SIP and HTTP are involved, a deeper inspection to extract insights into sessions and transactions can occur so routing of messages that belong to a particular session and/or transaction can be directed to specific service nodes. This contextual routing is beneficial in several use cases such as always being able to route SIP messages belonging to a conferencing session to the service node hosting that conference, or in routing-associated media stream to a common media server.
2. Offloading Encryption Overhead
Increasingly, encryption is becoming a key requirement for securing RTC and non-RTC traffic. For instance, encryption is called for in the emerging WebRTC-enabled communication solutions. Depending on the level of sophistication of the encryption and decryption techniques employed, they can result in a significant computation overhead, causing degraded performance.
Furthermore, due to different product upgrade cycle and maturity, all the nodes in a network are unlikely to provide same levels of encryption support. This makes it hard for network administrators to impose uniform encryption requirements across all supported services. They would need an efficient encryption engine designed for processing large volume of encryption traffic. A real-time ADC can be configured to offload encryption overhead from the individual service nodes, which can help to significantly improve application performance.
3. Interoperability
Finally, communication networks often depend on multiple media control protocols, resulting in complex, internetworking and integration challenges. Real-time communication protocol conversions such as between MGCP and SIP need to occur . A real-time ADC can convert the different protocols, , allowing applications to interoperate across protocols and keep the network running smoothly.
The telecom ecosystem has always responded to the challenges the new networks bring forth. New products and new ways of thinking have spurred innovation since I’ve been part of this industry. As telecom and IP continue to converge, specialization of existing elements will be required as voice becomes a component, not the reason for existence, of the overall network. The Real-Time Application Delivery Controller is one example








