Some fun weekend reading:
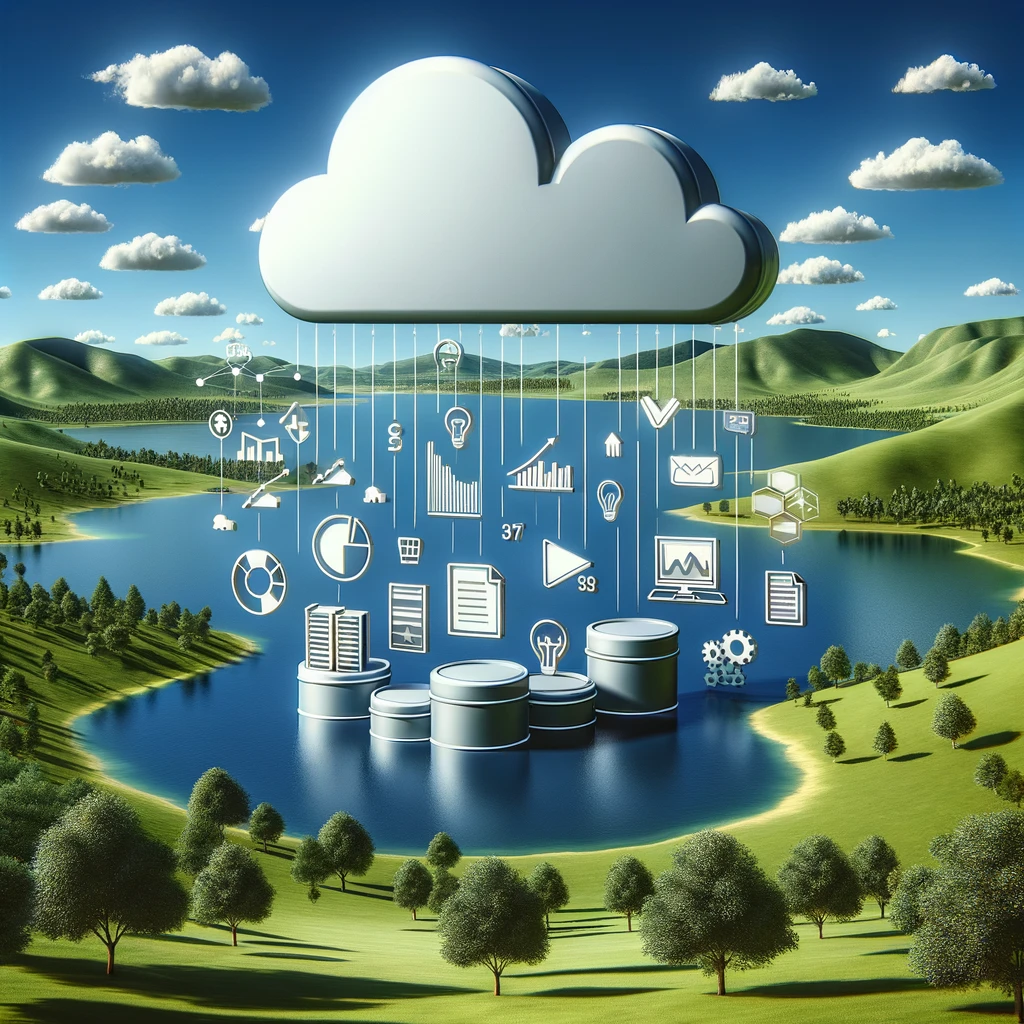
Snowflake was one of the companies that really popularized data lakes and they made themselves into an incredibly valuable company by riding on top of existing cloud vendors – by providing a data lake which is a centralized repository designed to store, process, and secure large volumes of data in its raw, native format. This includes structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Here’s a breakdown of what makes data lakes particularly useful and how they differ from other data management systems like data warehouses:
Characteristics of Data Lakes
- Storage of Raw Data: Unlike data warehouses, which store data in a highly structured format, data lakes retain data in its original format. This includes everything from text files and images to more complex records like logs and sensor data.
- Scalability: Data lakes are built on technologies that scale easily, often using cloud storage to manage vast amounts of data efficiently. This scalability makes data lakes suitable for industries that generate large amounts of data, such as social media platforms, healthcare, and finance.
- Flexibility: Users can store data without first having to design a detailed schema (schema-on-read), unlike traditional databases that require defining a schema before storing data (schema-on-write). This flexibility allows businesses to adapt quickly as their data processing needs evolve.
- Diverse Data Handling: They support various data types from different sources like IoT devices, social media feeds, corporate databases, and more.
- Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning: Data lakes facilitate complex analytical processing and machine learning directly on the raw data, which can drive more nuanced insights and predictive analytics.
Benefits of Data Lakes
- Cost-Effectiveness: Storing large volumes of data in a data lake, particularly in cloud-based solutions, can be more cost-effective than traditional data storage solutions.
- Improved Data Discovery and Quality: Allows comprehensive data discovery, analysis, and refinement tools, improving data quality and accessibility.
- Support for Real-time Processing: Many data lakes are designed to support both batch processing and real-time data processing, which is crucial for time-sensitive applications.
Potential Drawbacks
- Complexity in Management: Without proper governance, a data lake can become a “data swamp.” This occurs when the data is poorly organized, making it difficult to find, access, or use effectively.
- Security Concerns: Managing the security and privacy of data within a data lake can be challenging given the vast amount and types of data stored.
Use Cases
- Big Data Analytics: Companies use data lakes to store and analyze big data to identify trends, predict outcomes, and formulate strategies.
- Machine Learning: Data scientists use data lakes to train and deploy machine learning models that require access to large datasets.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Reporting: Industries that require real-time monitoring of data, such as telecommunications and manufacturing, utilize data lakes for immediate insights.
Data lakes are an essential part of modern data architecture, especially for organizations looking to leverage big data for competitive advantages. They offer a flexible, scalable environment for managing diverse datasets, which is crucial in today’s data-driven world.
More from AWS, InfoWorld and Forbes.
Aside from his role as CEO of TMC and chairman of ITEXPO #TECHSUPERSHOW, Rich Tehrani is CEO of RT Advisors and a Registered Representative (investment banker) with and offering securities through Four Points Capital Partners LLC (Four Points) (Member FINRA/SIPC). RT Advisors is not owned by Four Points.
The above is not an endorsement or recommendation to buy/sell any security or sector mentioned. No companies mentioned above are current or past clients of RT Advisors.